Football is one of the most practiced sports in the world, especially by youngsters. It offers a host of benefits, such as building endurance, working in teams, and instilling discipline. Injuries in young football players are, however, quite common during their formative years. Hence, players, coaches, and parents should comprehend what are common injuries, what causes them, and how they can be avoided. This article considers the common injuries faced by young footballers and outlines some simple ways in which they can be avoided.
Typical Injuries in Young Footballers
1. Osgood-Schlatter’s Disease
Osgood-Schlatter’s disease is the most prominent and frequent knee injury in young athletes aged between 10 and 15 years. It is marked by the onset of pain and swelling below the knee where the patellar tendon attaches onto the tibia. This occurs because the bones develop rapidly in growing children and teenagers in contrast to the muscles and tendons. This creates an enormous tension during intense activity such as football.

2. Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries
An anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury involves either a tear or a sprain in one of the ligaments within the knee. These injuries have an abundance of occurrences amongst adult football players. But it is not unusual while occurring in teenagers, particularly those in competitive football. It usually happens when players quickly change direction, land awkwardly or collide with other players.

3. Ankle Sprains
Ankle injuries are amongst the exacerbated types of injuries that occur during football. When the ankle twists or turns awkwardly, ligaments are either simply stretched or completely torn. Vulnerable are the young players as they attempt quick turns, abrupt stops, or walk along irregular grounds.
4. Groin Strains
These occur when the muscles of the inner thigh are stretched beyond their limits. In side-to-side movements and those that require kicking and acceleration, the groin strain is the most common one noted in football.
5. Muscle Strains (Hamstrings and Quadriceps)
Strains of the hamstrings and quadriceps are quite common in this sport due to actions like sprinting, kicking, and rapid acceleration. These strains may range from a mild inconvenience to a more serious tear in the muscle.
6. Growth Plate Injuries
Growth plate injuries exist only in children and teenagers because their bones are still developing. These plates are weaker than the rest of the bone, making them more susceptible to fractures. It is evident especially during sports involving bodily contact, like football.
Reasons for Injuries in Young Footballers
Overtraining
Injuries to young footballers mostly occur in cases of overtraining. Most youngsters would be playing for their school teams, club teams, and even extra training sessions. Without proper rest, muscles and joints do not get enough time to recover, increasing the risk of injury.

Rapid Growth Spurts
During puberty, children experience rapid growth spurts. Bones grow quickly, and muscles, tendons, and ligaments take time to adjust. This imbalance can make young players more prone to injuries, especially in the knees and ankles.
Poor Warm-Up and Cool-Down Habits
Skipping warm-ups and cool-downs is a frequent mistake among young players. Warm-ups prepare muscles for intense activity, while cool-downs help reduce muscle soreness. Without these, players face a higher risk of strains and sprains.
Bad Playing Conditions
Uneven fields, poor-quality footwear, and hard surfaces can contribute to common football injuries. Playing in such conditions increases the chances of falls, twists, and collisions.
Poor Technique
In young footballers, improper techniques in running, jumping, and tackling can cause unnecessary strain on joints and muscles, leading to avoidable injuries.

How to Prevent Injuries in Young Footballers
1. Proper Warm-Up and Stretching
Before training or matches, young players should always warm up. This includes light jogging, dynamic stretches (like leg swings and lunges), and mobility exercises. A proper warm-up increases blood flow to muscles and prepares the body for the demands of football.
2. Regular Strength and Conditioning
Strength training helps improve muscle balance and joint stability. Exercises like squats, lunges, and core workouts make muscles stronger and protect joints. Conditioning drills like agility ladders, cone drills, and sprint exercises improve coordination and reaction time, reducing injury risk.
3. Focus on Flexibility
Stretching after training sessions is crucial. Simple stretches targeting hamstrings, quads, calves, and hips keep muscles flexible and help avoid strains. Yoga is also a good way to improve flexibility and balance.
4. Avoiding Overtraining
Rest days are as important as training days. Coaches and parents should monitor weekly training loads and ensure players have at least one or two rest days every week. Overtraining can lead to long-term injuries like tendinitis and stress fractures.
5. Recovery is Key
Young footballers should follow good recovery habits. This includes proper hydration, balanced nutrition, and quality sleep. Ice packs, foam rolling and physiotherapy massages can also help muscles recover faster after intense sessions.

6. Use Proper Equipment
Wearing the right boots according to the playing surface reduces the chance of ankle sprains. Shin guards protect against direct impact injuries. A proper fit in equipment is essential for comfort and safety.
7. Learning the Right Techniques
Coaches should teach young players correct techniques for running, turning, tackling, and jumping. Focus should be on balance and body control, which help prevent awkward movements that cause injuries.
8. Listen to Your Body
Young footballers must be encouraged to report any pain or discomfort early. Playing through pain can make minor injuries worse and cause longer recovery times. Parents and coaches should foster a culture where it’s okay to rest and seek help.
9. Physiotherapy and Medical Check-ups
Regular physiotherapy check-ups can help identify muscle imbalances or tightness. It is better to identify before they lead to injury. Physiotherapists also guide young players on injury-prevention exercises and recovery routines. Annual sports medical check-ups can spot underlying issues early.
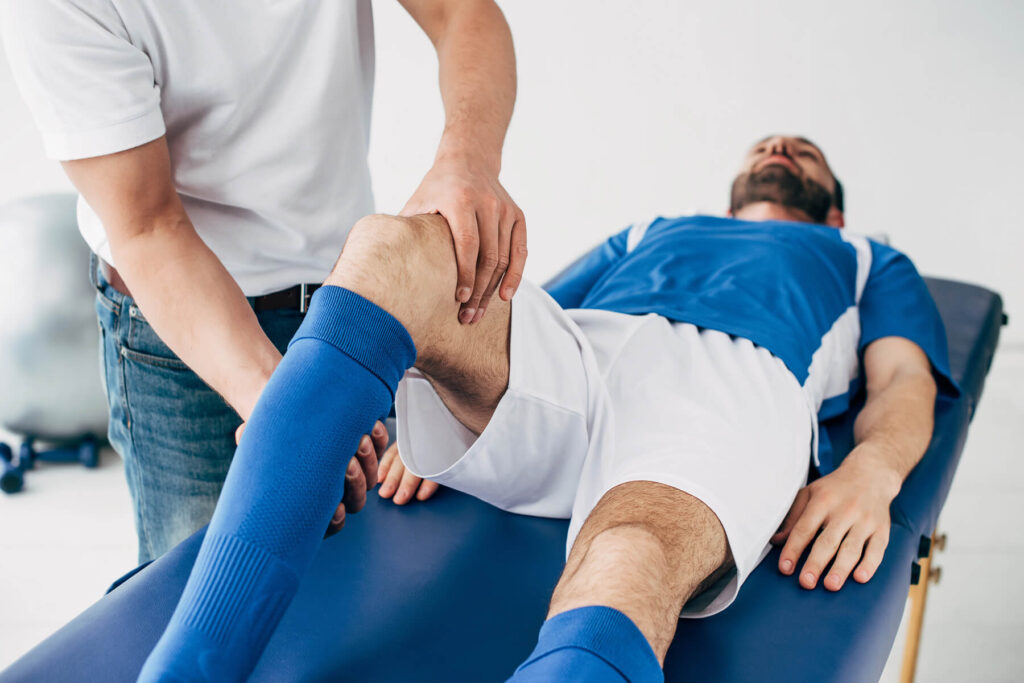

Importance of Recovery and Conditioning
Recovery is often overlooked but is essential in preventing injuries. Rest allows the body to repair muscle tissues and reduce inflammation. Good conditioning builds strength, flexibility, and endurance, allowing young players to perform better and avoid injuries.
A combination of rest, good nutrition, proper hydration, and adequate sleep supports faster recovery. Parents and coaches should monitor the early signs of fatigue. They should avoid pushing young players to continue when they are clearly tired or in pain.
Conditioning should be included throughout the season, not just before it starts. A well-conditioned player has better posture and improved movement mechanics. They also have a lower chance of muscle strains or ligament tears.
Staying Injury-Free for Football Success
Injuries are a part of sports, but many injuries in young footballers are preventable with the right approach. Common issues like ACL injuries, ankle sprains and muscle strains can be avoided through proper warm-ups, strength training, flexibility work, and rest.
Overtraining and growth-related injuries are major risks during teenage years. But recovery routines, smart training schedules and age-appropriate exercises can help keep young players safe. By building good habits early – maintaining fitness and using proper techniques – young footballers can enjoy the game, avoid long breaks due to injury, and develop their talents to the fullest.
